Caring for the Elderly
Statistics
The 5 Types of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Dementia Based - This type effects broad cognitive functioning across significant and wide-ranging parts of the brain. The neurons, specifically. Diseases of this type can primarily effect memory centers in the case of Alzheimers, or additionally affect general cognitive skills in addition to one’s memory.
Demyelinating - This type attacks primarily the Myelin sheath surrounding the nerves, which is responsible for enabling signal transmission between neurons and muscle receptors. Diseases of this type tend to affect motor skills and coordination. Cognition is also affected, but as the neurons are not attacked directly, the issues tend to center around their ability to communicate with each other, resulting in symptoms like brain fog, or fatigue.
Parkinson’s Type - This is similar to dementia based, in the sense that specific brain neurons are damaged and attacked. But the effects of this type are more similar to the Demyelinating type in the sense that motor skills and fine coordination skills are especially attacked. Motor neuron diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and progressive supranuclear palsy also fall into this broad type.
Prion Dieases - Misfolded proteins accumulate and deal severe damage over time to the general cellular structures of the brain and nervous system. These disease usually have a very short time from onset to death, and many patients do not survive past 1 year from onset.
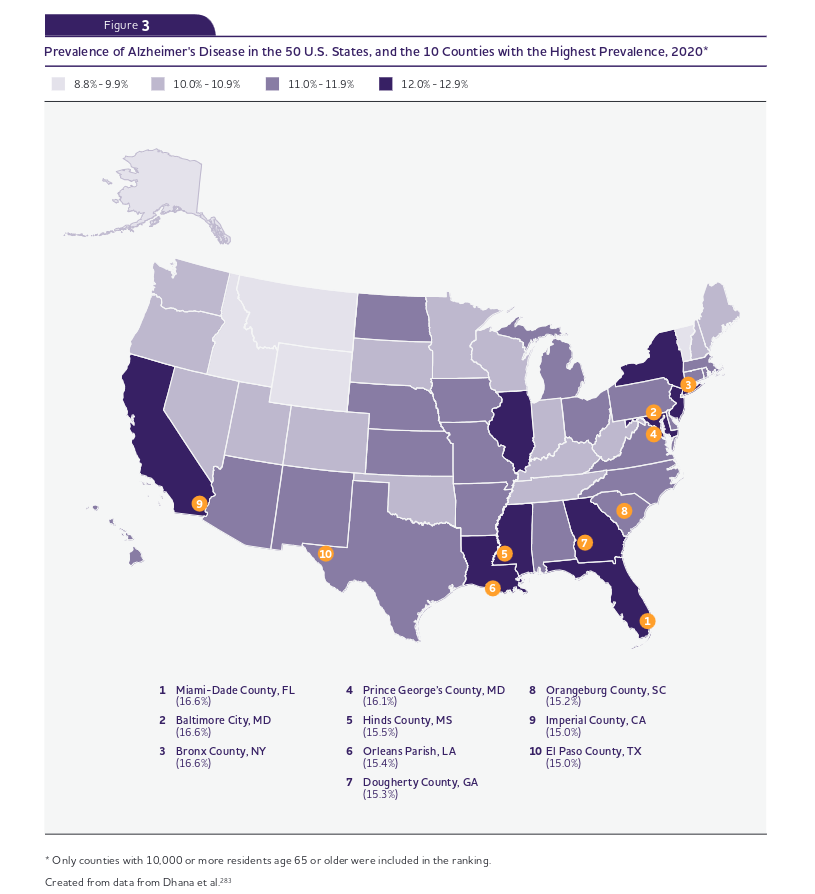
Incidence Rates of Alzheimer’s in the United States
The figure below shows the incidence rates of Alzheimer’s diagnosis for new patients within the United States, along with the 10 counties with the highest incidence rate, as well:
For more information, there is an excellent pdf by the Alzheimer’s Association [of America], and which is really well written.
Alzheimers Facts and Figures:
Treatment Preference for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Multicriteria Decision Analysis with Caregivers, Neurologists, and Payors.